Introduction:
To manage inherent complexities of software development,
scalability, maintainability, reusability, cost efficiency
etc. throughout the software's lifecycle, architectural
approaches play a very crucial role. The fundamental principle
of a good software architecture is to reduce complexity and
enable changes to be made with minimal impact on the overall
system. To build a new application, one must decide if they
want to choose the standard Monolithic architecture or one
that leverages microservices. Though both approaches have
their advantages and disadvantages, the choice between
monolithic and microservices should be based on the project's
specific requirements and architectural goals. Let’s
understand the two architectures in more detail so we can
select the best option for your business:
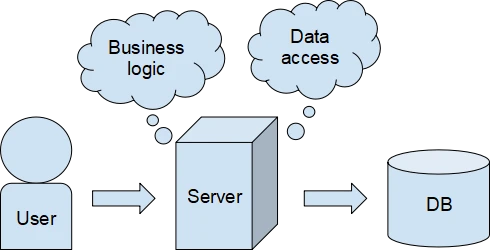
Monolithic architecture:
Monolithic architectures have been used for many years and can
be well-suited for certain types of applications, especially
those with relatively simple requirements or when rapid
development and deployment are a priority. It is a traditional
software design model where an application is built as a
single, self-contained unit that operates independently from
other applications or services. The model is designed as a
single block, with all the components tightly coupled into a
single unit. These applications have a single code base shared
by multiple teams. Hence a single change to the application
code requires the whole application to be re-released. Because
of this, updates and new releases typically can only occur
once or twice per year and may only include general
maintenance instead of new features.
Monolithic architecture comes with both advantages and
disadvantages. Let’s discuss them in detail:
Advantages:
-
Simple to use: Monolithic applications are
generally simpler to develop, as all components are tightly
integrated within a single codebase.
-
Testing: Testing a monolithic application
is easier because all components are tightly coupled and
exist within the same environment.
-
Simplified Deployment: : Deploying a
monolithic application is generally easier because it
involves deploying a single unit.
-
Code Reusability: Since Monolithic
applications share the same codebase it’s easier to reuse
code across different components.
-
Suitable for small or simple Applications: Projects with straightforward
requirements
where the
complexity of microservices may be unnecessary can opt for
Monolithic architecture.
Disadvantages:
-
Complexity: Single codebase can become
difficult to manage and understand, especially for large and
long-lived projects.
-
Fault tolerance: Due to tight coupling,
failure in one component can potentially impact the entire
application.
-
Scaling: Monolithic architecture supports
vertical scaling which can incur more cost.
-
Adopting new technologies: Upgrading or
adopting new technologies for specific components of the
application is complex and time-consuming.
Microservices Architecture:
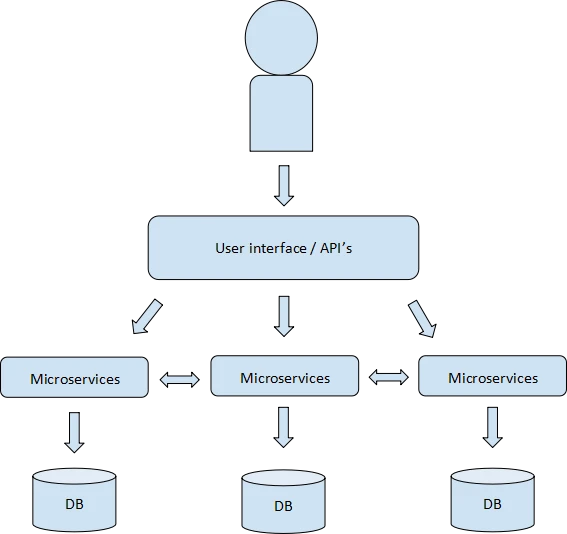
Microservices architecture is a viable solution for many
modern applications. It breaks down a complex application into
smaller, independently deployable components, each responsible
for a specific task. These components (also known as
microservices) communicate with each other through
well-defined APIs to collectively provide the full
functionality of the application.
Microservices are loosely coupled and benefit both dynamic
scalability and fault tolerance. This approach also allows you
to change minor components of the application without
rebuilding and redeploying the entire system thus delivering
quality software faster.
Microservices have substantial advantages over traditional
monolithic applications along with few limitations. Let's
discuss them in detail:
Advantages:
-
Independent components / services: Microservices are designed to be independently
developed
and each service has its dedicated team responsible for its
development and maintenance.
-
Independent Scalability: Microservices lets
each service be scaled independently. This approach prevents
scaling the entire application when only one component
requires additional resources.
-
Reliable: The loosely coupled nature of
microservices makes them more reliable which means If one
service fails, it doesn't necessarily impact the entire
application.
-
Flexible development: Developers can
choose different tools for the specific requirements of each
service leading to faster and more efficient application
development.
Disadvantages::
-
Time consuming: The process of creating and
managing numerous microservices can be time-consuming.
-
Complex Testing:Microservices follow a
two-tier testing approach where every service must be tested
individually, and then integration testing is required to
verify how they work together as a whole.
-
Complex Versioning and Compatibility: It is
challenging to manage changes and versioning of individual
microservices and maintain compatibility of each service.
-
Complex deployments: Each microservice
must be integrated into a functional application before
deployment hence with the growing complexity of the
application, the complexity of the deployment process also
grows.
Conclusion:
While both Monolithic and Microservices architectures have
pros and cons of their own, the choice of architecture should
align with the specific needs and project goals. To make any
informed architectural choice that aligns with the project's
needs and goals, there are few things to be considered:
-
Application Complexity: Simple
applications, like web forums or basic eCommerce stores, may
be well-suited for monolithic architecture, which is easier
to build and deploy. Microservices are often favored for
more complex applications due to their modularity and
scalability.
-
Business goals: MIf your business is
aiming for significant growth, the benefits of
microservices, such as faster development cycles, better
fault isolation, and improved scalability, will outweigh the
costs and complexities of monolithic architecture.
-
Cost and Time to Develop: Monolithic
applications are often faster and less resource-intensive to
create initially. However, they may become costlier as they
grow. Microservices can be more resource-intensive upfront
but may result in cost savings as the application scales and
evolves.
-
Team Size and Skills: Building a
microservices-based application will be difficult If your
team has less experience with microservices whereas
Monoliths are a good choice for single developers or small
teams.
Therefore, where Microservices are often suitable for large
and complex applications, Monolithic architectures can be a
good choice for smaller projects.