Introduction to Kubernetes
Kubernetes or k8s is an open source platform that is used to
configure and automate container operations. It was developed
by Google in 2014. It is used for scaling and deploying
containerized applications. Automating container operations
usually include orchestration of networking, computing and
storage infrastructure on behalf of user workloads. A group of
hosts running containers are clustered together and Kubernetes
manages those clusters.
Why to use Kubernetes?
Real production applications span multiple containers which
need to be deployed across multiple server hosts. Kubernetes
manages to scale and deploy these containers for the
workloads. Kubernetes orchestration allows us to build
application services that span multiple containers, schedule
and scale those containers across a cluster and manage to
spawn up instances in case any one of the instance from a
cluster fails. Kubernetes can be thought of as:
- a container platform
- a microservice platform
- a portable cloud platform
Containers can be grouped to form a "pod" and then schedule
workload while providing services like storage and networking
to the containers inside. Kubernetes also allows load
balancing across pods.
Kubernetes Architecture
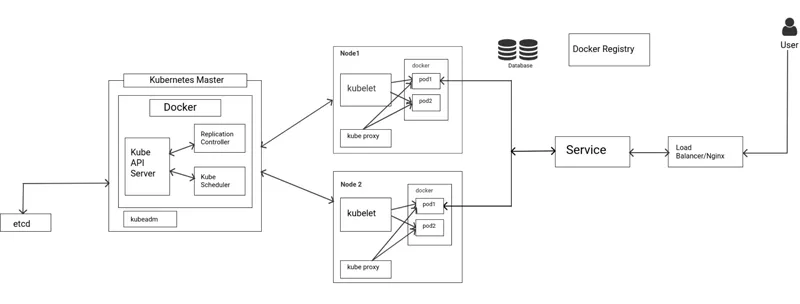
-
Kubernetes follows a client-server arcitecture. There is 1
master which controls1 or more nodes. It is possible to have
multiple master nodes for high availability.
-
There is a Docker Registry which is a kind of central
repository which containsDocker images.
-
Master node contains 5 main components:
Kube API Server: It is a central management entity that
receives REST API requests and serves as a front-end for
the cluster. It is the only component that communicates
with the etcd cluster and makes sure that cluster state
and data is stored in it.
Replication Controller: It is a type of
kube-controller-manager that is responsible for
pod-replication to maintain shared state of cluster and
to check if all tasks are performed. When a change in
service configuration occurs or if a node fails, it sees
to it that a new node is spawned up and the cluster
state is changed to the desired state.
Kube Scheduler: It is responsible for scheduling a pods
on various nodes based on resource utilization. It
considers the request requirements and assigns it the
best-fit node. For ex, if an application needs 2GB ram,
then it will look for nodes that satisfy this
requirement with available resources. The scheduler must
know the total available as well as the number of
utilized resources.
Kubeadm: It is responsible for pod administration as
well as for initializing clusters.
Etcd: etcd is a cluster which stores other clusters data
and API objects. It isaccessible only from API Server
for security reasons.
Node contains 3 main components as follows:
Kubelet: It is an agent that runs on each node in a
cluster. It makes sure that the containers are running
inside pods.
Kube-proxy: It enables service abstraction by
maintaining network rules on the host and performing
connection forwarding. It also exposes services to the
external world.
Pods: It encapsulates containers, resources,
configurations of how to run containers. Each pod has a
unique ID associated to it. A continer contains simply a
docker image.
Whenever a user hits a requsest, it first goes to a Load
Balancer. Here we have used Nginx as our Load Balancer. It
is the duty of the load balancer to look after the traffic
distribution of the requests. For more information,
refer this.
Nginx is a kind of a load balancer which sits in front of
your server and distributes client requests across a group
of services. The main advantage of using Nginx is that it
maximizes speed and capacity utilization. For more
information on Nginx, please
refer this.
Conclusion
On a concluding note, we can find answers to 2 crucial
questions based on k8s architecture as follows:
Why do we build a microservice using Kubernetes?
-
We can run pre-built and configured components in containers
as a part of every release. With every deployment, a new
container is deployed which saves the overhead of doing
manual configurations.
-
We provide all the kubernetes cluster configurations through
.yaml files, whichis usually called as the desired state of
the cluster.
-
Kubernetes maintains the desired and actual states of
cluster and sees to it if they are always in
synchronization. Thus, if any instance fails, the
replication controller(which is a kind of
kube-controller-manager) replicates the pod of thefailed
instance, thus running the application successfully. It
makes k8s maintain reliability of the system.
-
Kubernetes offers autoscaling of workload based on CPU
utilization and memory consumption.
-
It allows vertical scaling-increasing the no. Of CPU's for
pods and horizontal scaling-increasing the no. of pods.
- Thus, microservices can run better with kubernetes.
Why is it best practice to keep Database out of kubernetes
cluster?
-
In care of Kubernetes volume, when a pod is deleted, all the
data is lost too.
-
Thus, we use Persistent Volumes, which will keep the data
even if a pod is spawned.
- It stores the data on our local storage.
-
There is one Persistent Volume for one mysql. So, if the
data inside the database will increase, the size of the
local storage will also be needed to be increased.
-
Thus, it is a best practice to keep database outside the
kubernetes cluster.



